UX / Štýly interakcie a ľudské vnímanie
Štýly interakcie
a ľudské vnímanie
Používateľské rozhrania a používateľský zážitok
Sergej Chodarev (sergejx.net), Michaela Bačíková
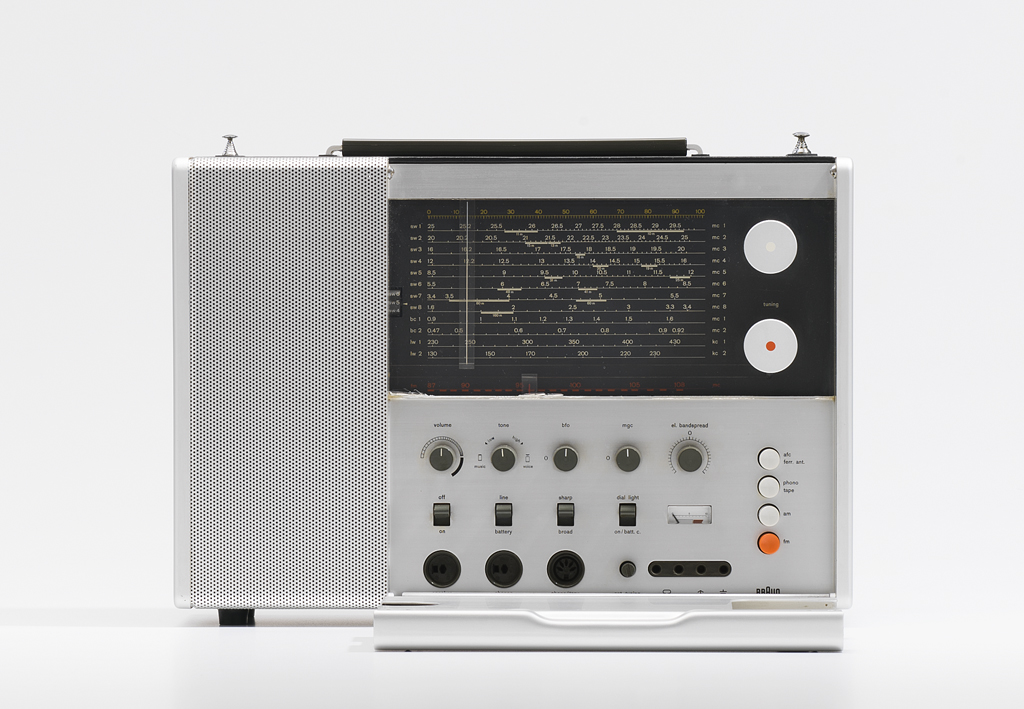
Dávkové systémy
- žiadna interaktivita
- zadanie sady úloh
- získanie výsledku neskôr
Odporúčania
- Možnosť sledovať stav
- Možnosť prerušiť alebo zmeniť úlohy
Otázka–odpoveď
- počítač riadi používateľa
Jazyk príkazov
- Možnosť komplexných príkazov
- História príkazov
Celoobrazovkové rozhrania
Funkčné klávesy
- Rýchle
- Vhodné ako doplnok (klávesové skratky)
Formuláre
- Viacero položiek
- Viditeľné a editovateľné naraz
Menu
- Používateľ si nemusí pamätať príkazy
- Potenciálne mätúca hierarchia
- Môžu byť aj textové alebo zvukové
Grafické používateľské rozhrania
WIMP
- Windows
- Icons
- Menus
- Pointing device
Priama manipulácia
- Ťahaj a pusti (drag-and-drop)
- Posúvanie objektov priamo, voľby príkazov príkazov
- Zoom dvoma prstmi
„Objektovo-orientované rozhrania“
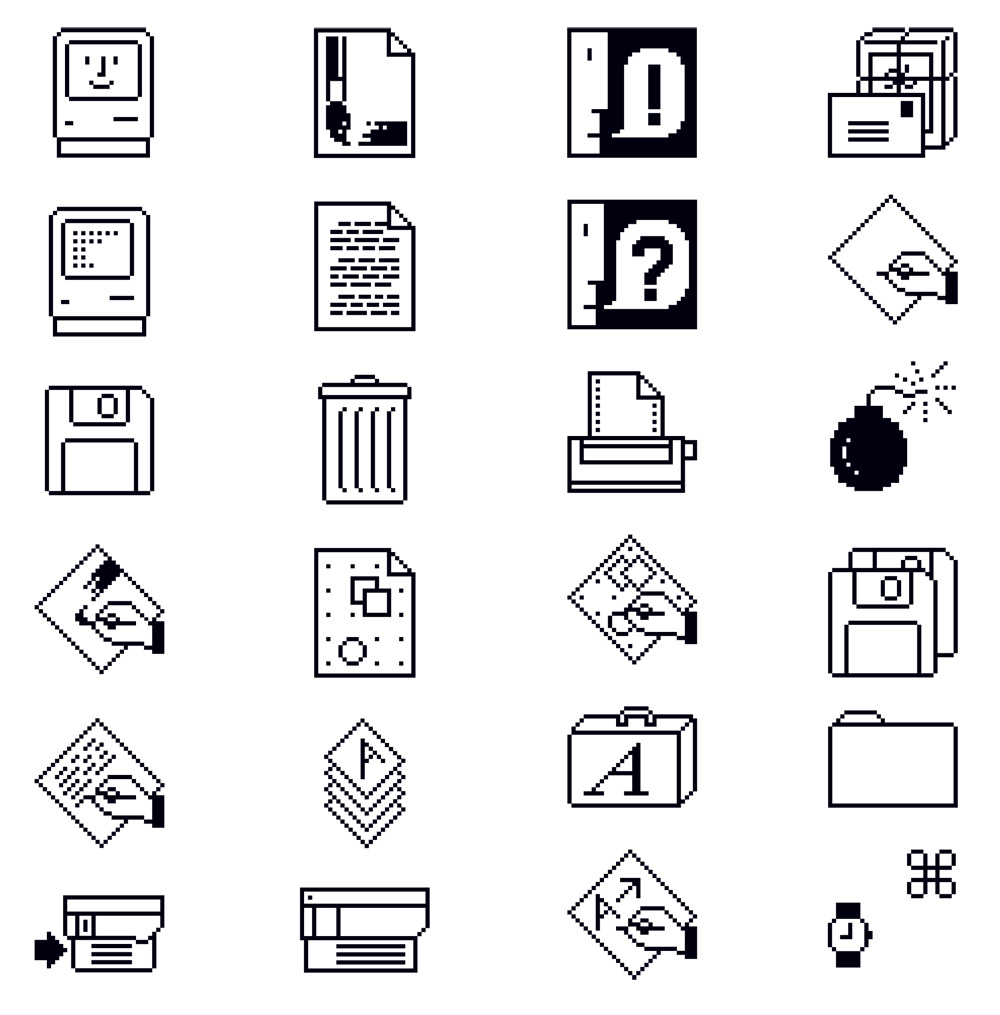
Ikony
- Symbolická reprezentácia objektov a akcií
Mapovanie
- Podobnosť (napr. papier reprezentuje súbor)
- Analógia (napr. nožnice pre vystrihnutie)
- Ľubovoľné (napr. krížik pre odstránenie)
Často je veľmi zložité nájsť vhodný symbol
Súťaž ikoniek
Nakreslite ikonky pre obrazovku digitálneho fotoaparátu, ktoré budú reprezentovať tieto akcie:
- Odstrániť poslednú fotografiu
- Odstrániť všetky fotografie z pamäte
- Formátovať pamäťovú kartu
Pošlite svoje návrhy do Discordu #icons-contest
Nové alternatívy
- Virtuálna realita
- Hlasové ovládanie
- Prirodzený jazyk
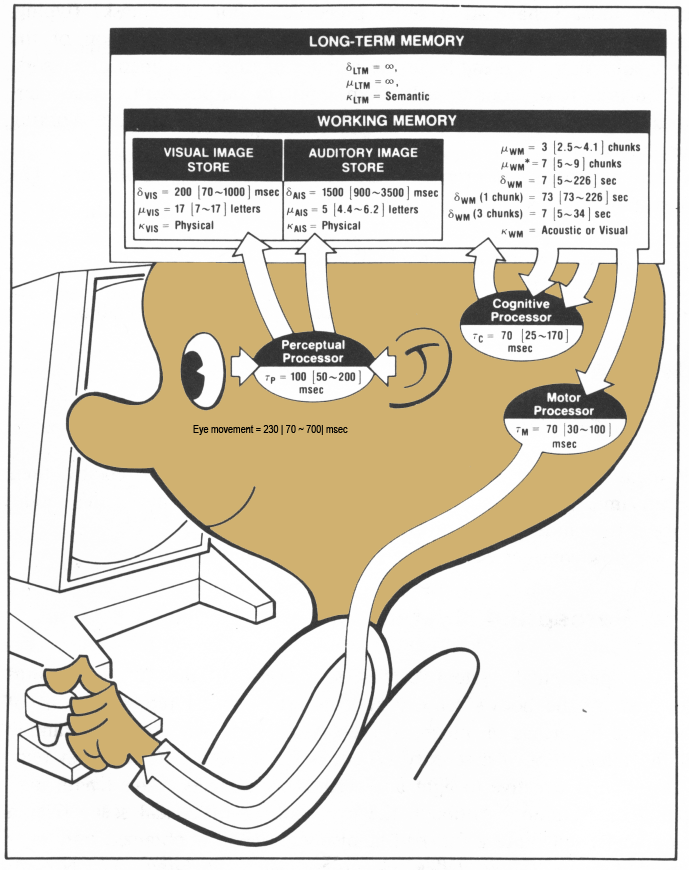
Model Human Processor (MHP) (Card a kol.)
P1: Variable Perceptual Processor Rate Principle
The Perceptual Processor cycle time varies inversely with stimulus intensity.
P2: Encoding Specificity Principle
- Specific encoding operations determine what is stored.
- What is stored determines what retrieval cues are effective in providing access to what is stored.
P3: Discrimination Principle
The difficulty of memory retrieval is determined by the
- candidates that exist in memory
- relative to the retrieval clues.
P4: Variable CP Rate Principle
The CP cycle time is shorter when greater effort is induced by increased task demands or information loads; it also diminishes with practice.
- CS is parallel in its recognition phase
- and serial in execution phase
- (perceive multiple things at once, but do just one at a time)
Human models
Performance is calculated based on:
- perception (speed, accuracy)
- motoric abilities
- simple decisions
- learning
Fitts law for pointing (1954)
The time to move the hand to a target of size S decreases with:
- shorter distance D
- larger target size W

Uncertainty principle, Hick’s Law (1968)
- Decision time increases with
- uncertainty about the judgement or decision to be made
Application: the decision is harder when there are
- Many possibilities to choose from
- Less information about the problem
 Ikona Najsvätejšej Trojice. Andrej Rubľov, 1425—1427. © wikipedia
Ikona Najsvätejšej Trojice. Andrej Rubľov, 1425—1427. © wikipedia